As the airtightness of a building improves, the importance of a properly functioning ventilation system also increases. A properly functioning ventilation system ensures a controlled indoor climate and a good balance between the air supplied in the living rooms and the air discharged in the wet rooms.
Ventilation reporting of residential buildings
A ventilation system ensures a controlled inflow and outflow of fresh air on the one hand, and polluted / wet air on the other. The system works optimally when there is a balance between supply and discharge. This ensures that there is no unwanted overpressure or underpressure in the building.
A ventilation system - whether demand-driven or not - limits heat losses in the winter and ensures cooler indoor air during the summer. The system also increases the feeling of comfort in the home and reduces the risk of condensation and respiratory problems. It is therefore no surprise that a properly installed ventilation system reduces E-level points.
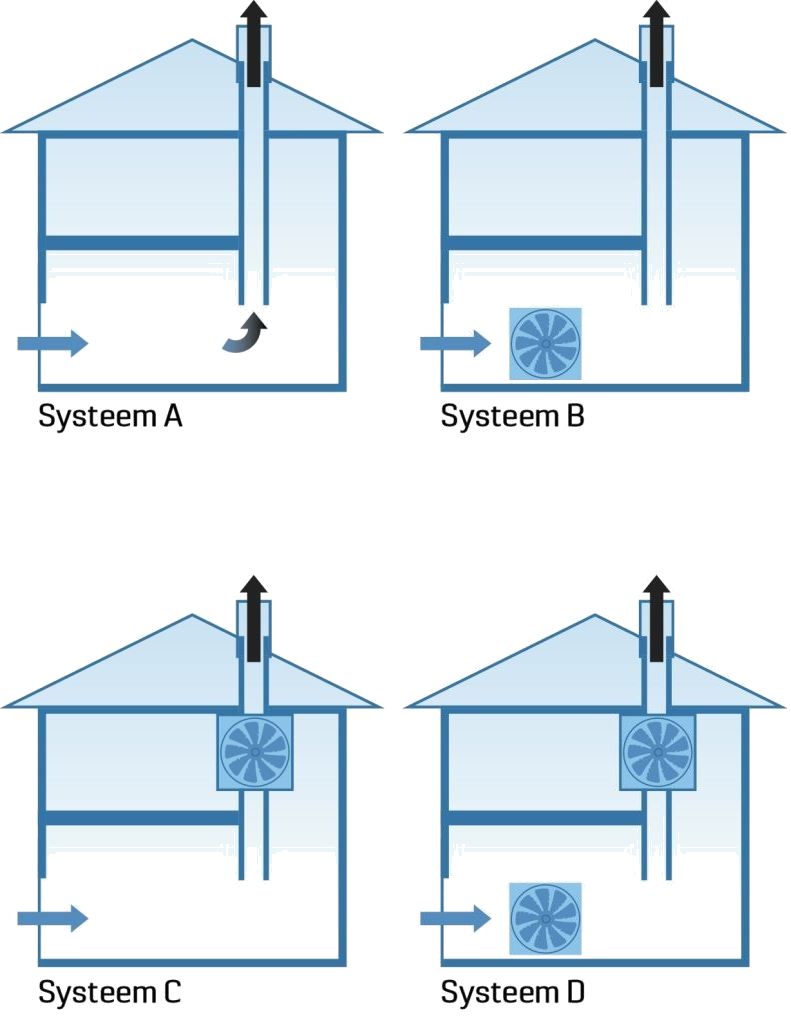
A distinction is made between 4 types of ventilation:
- System A (natural ventilation)
- System B (mechanical supply and adjustable discharge)
- System C (adjustable supply and mechanical discharge)
- System D (mechanical supply and discharge)
In practice, almost exclusively opted for system C and D.
Why ventilate?
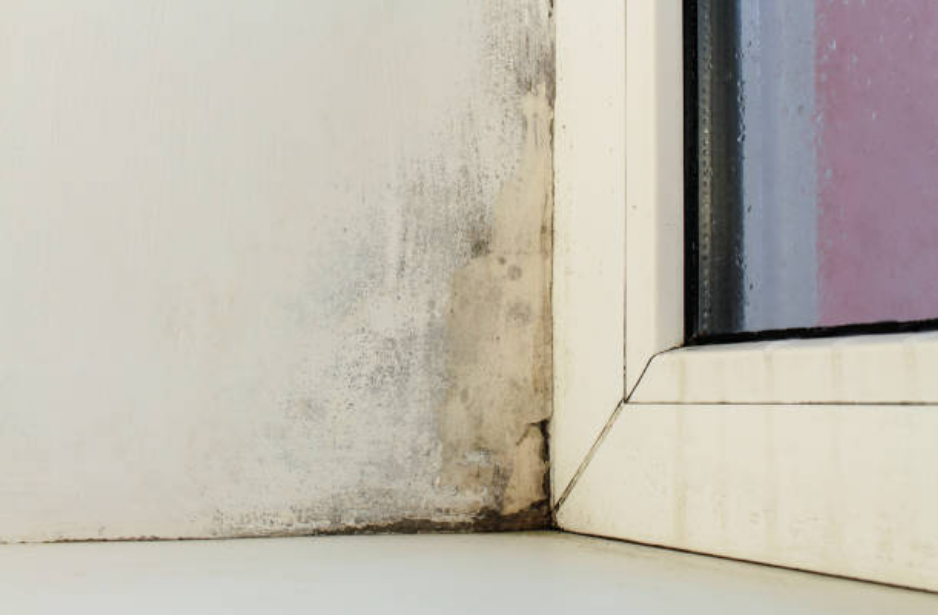
Our houses are increasingly insulated and built more airtight, which reduces the energy bill. That is good news for the environment and our wallet. But good insulation combined with airtight construction will soon lead to problems with the air quality if there is insufficient ventilation.

The benefits of (good) ventilation can be summarized as follows:
»Supply of fresh, clean air
» Discharge of wet, polluted air
»Increasing comfort by removing unwanted odors, CO² and other gases
»Reducing the risk of mold and respiratory problems
» Limiting heat losses through a controlled indoor climate
»Energy saving by preheating or cooling supply air
» Extracting E- level points for correct functioning
Ventilation reporting
Since 01/01/2016, it is mandatory for a ventilation reporter to have the ventilation system tested for new construction and energy renovations. Depending on the type of system chosen, the mechanical ventilation, any supply and discharge grilles and the flow areas of the home are measured and reported in situ.
With a well-designed ventilation installation, a reduction of realize the E-level up to 15 E-level points. Perhaps you can therefore benefit from a number of subsidies when you achieve a sufficiently low E-level. Your EPB reporter can provide you with more details.
In addition to an EPB reporter, a ventilation reporter must also be appointed. This is appointed for at least one of the following components:
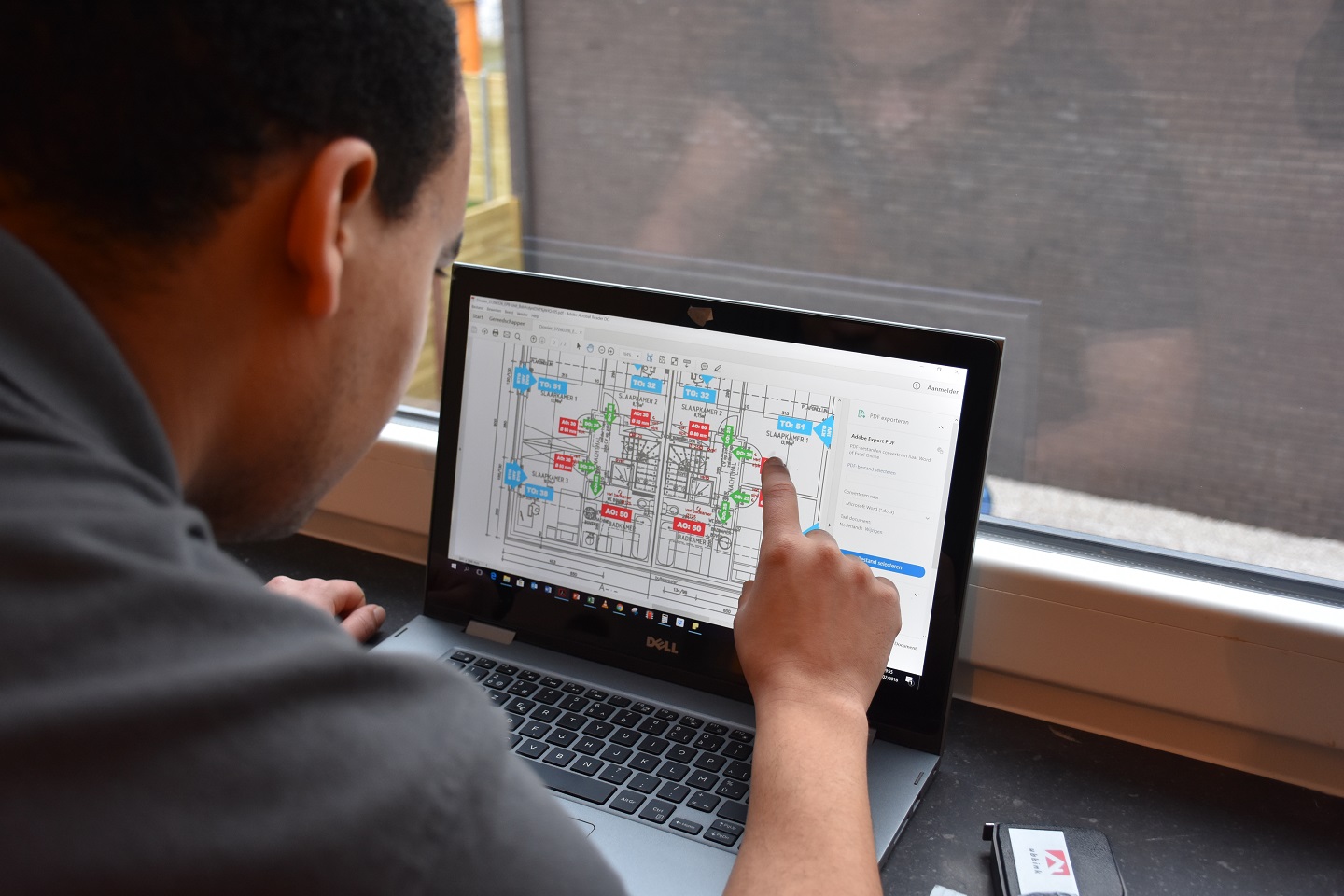

Ventilation Preliminary (VVO)
A ventilation plan where supply, flow and discharge are visually displayed on a floor plan of the building together with the required flow rates.
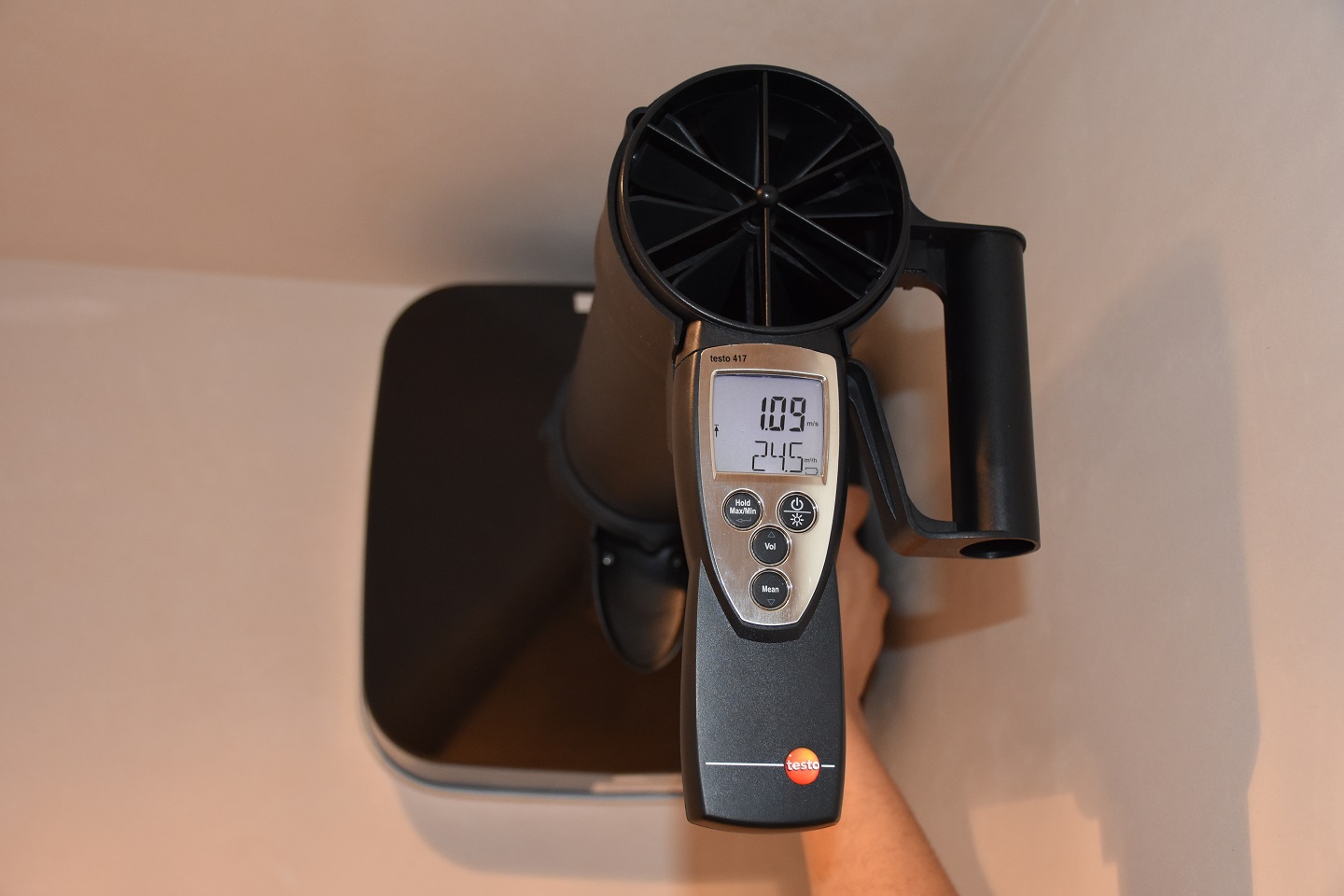

Flow measurement Mechanical Ventilation (MV)
The mechanical flow rates in every room are measured on the ventilation grilles. If the schedules are adjustable, they are adjusted where necessary to achieve the required flow rates and / or balance. The capacity of the ventilation group is also measured if possible. All calculated and measured values are processed in a report and submitted to an external quality framework.
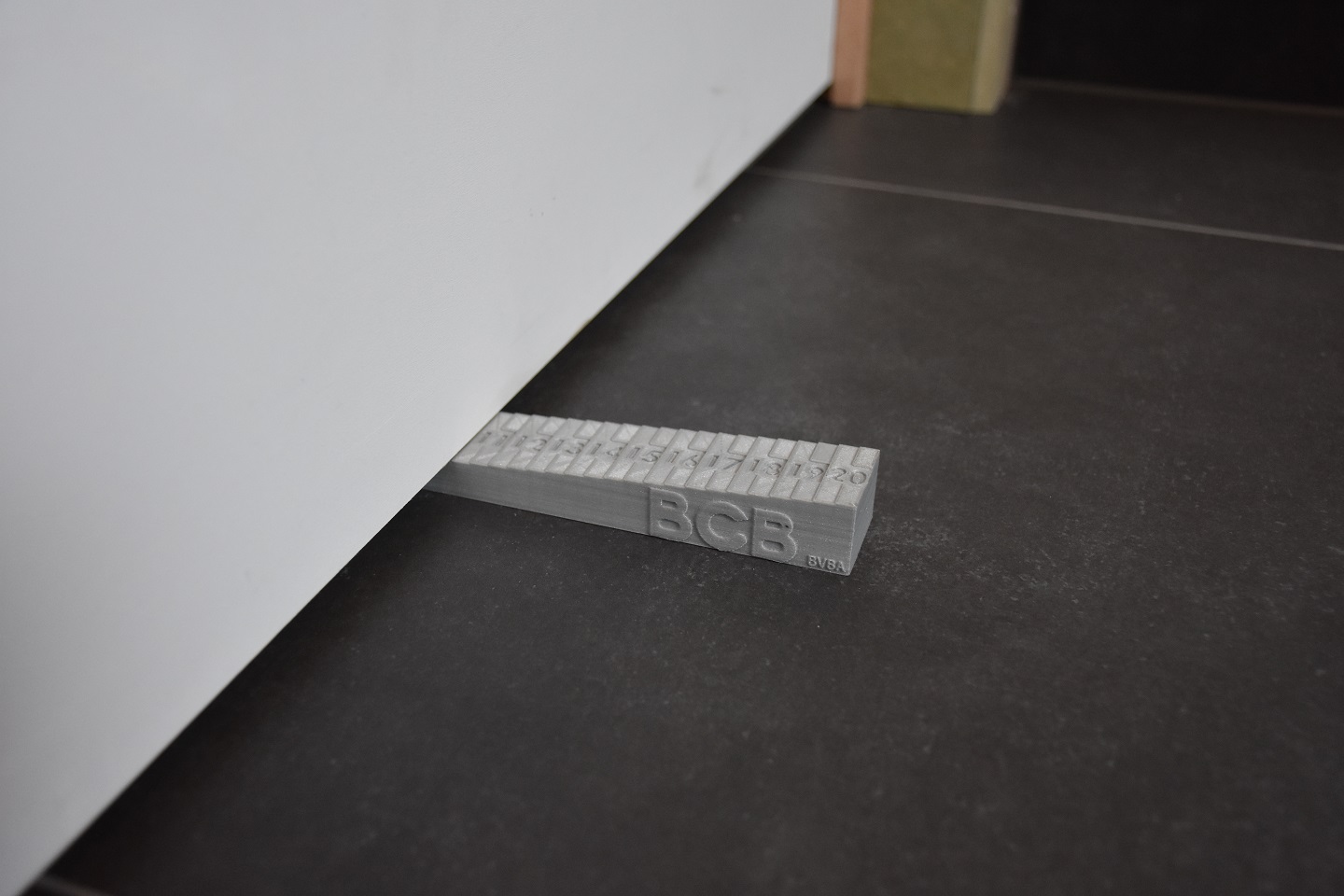

Flow measurement flow openings (DO)
The actual passages for the air flow (gaps under the door, openings in the door or wall) are measured, calculated and subsequently submitted to an external quality framework.
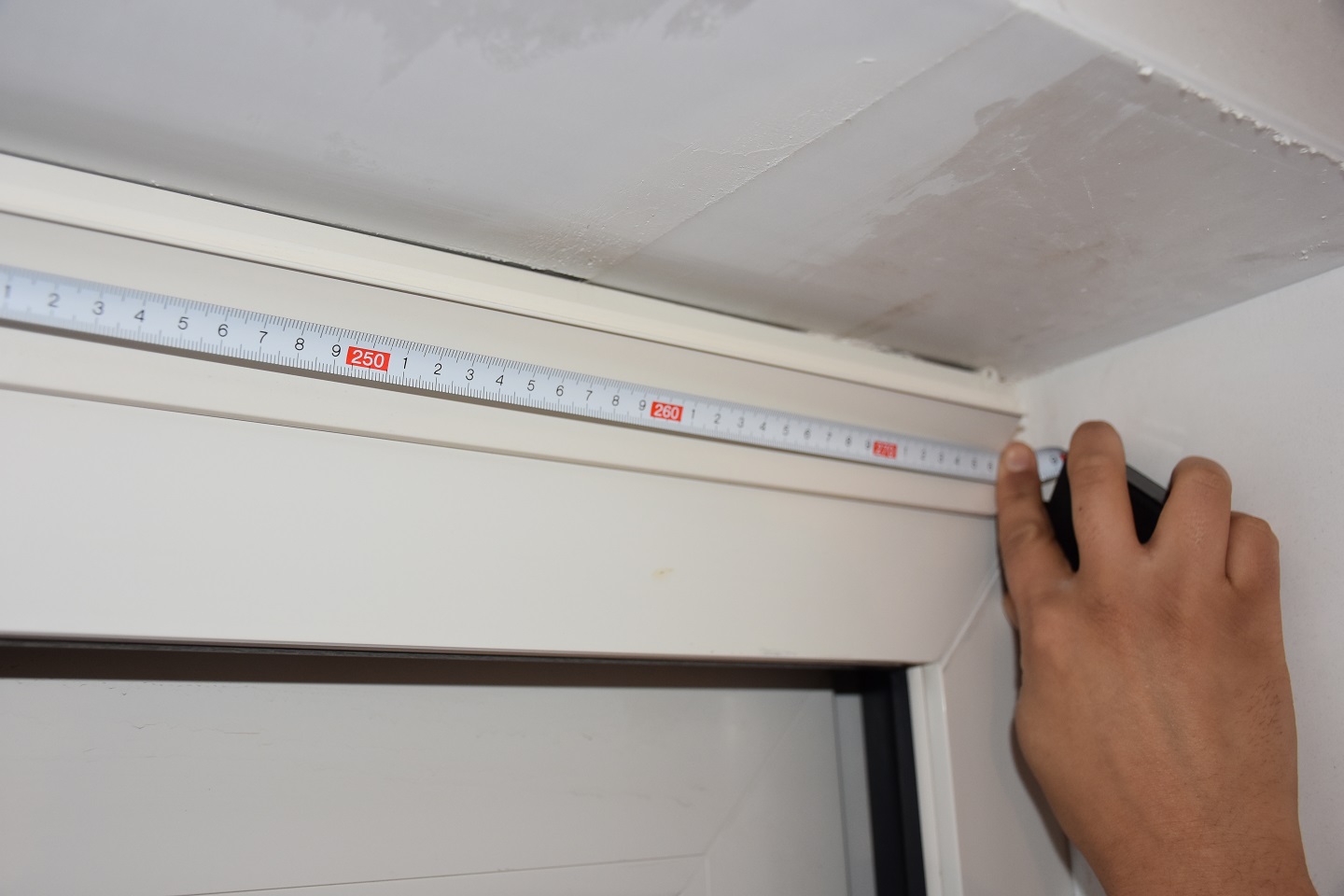

Flow measurement Adjustable Ventilation Grids (RTO)
The length of the grid is measured, the type of grid is noted and the flow rates are calculated. These results are then submitted to an external quality framework.
Performing a ventilation report
The reporting must always be carried out by a recognized ventilation reporter. There should be close cooperation between EPB reporter and ventilation reporter.
» The measurements / reporting are always done in accordance with STS-P 73-1» Files are followed up and approved by a mandatory external quality framework
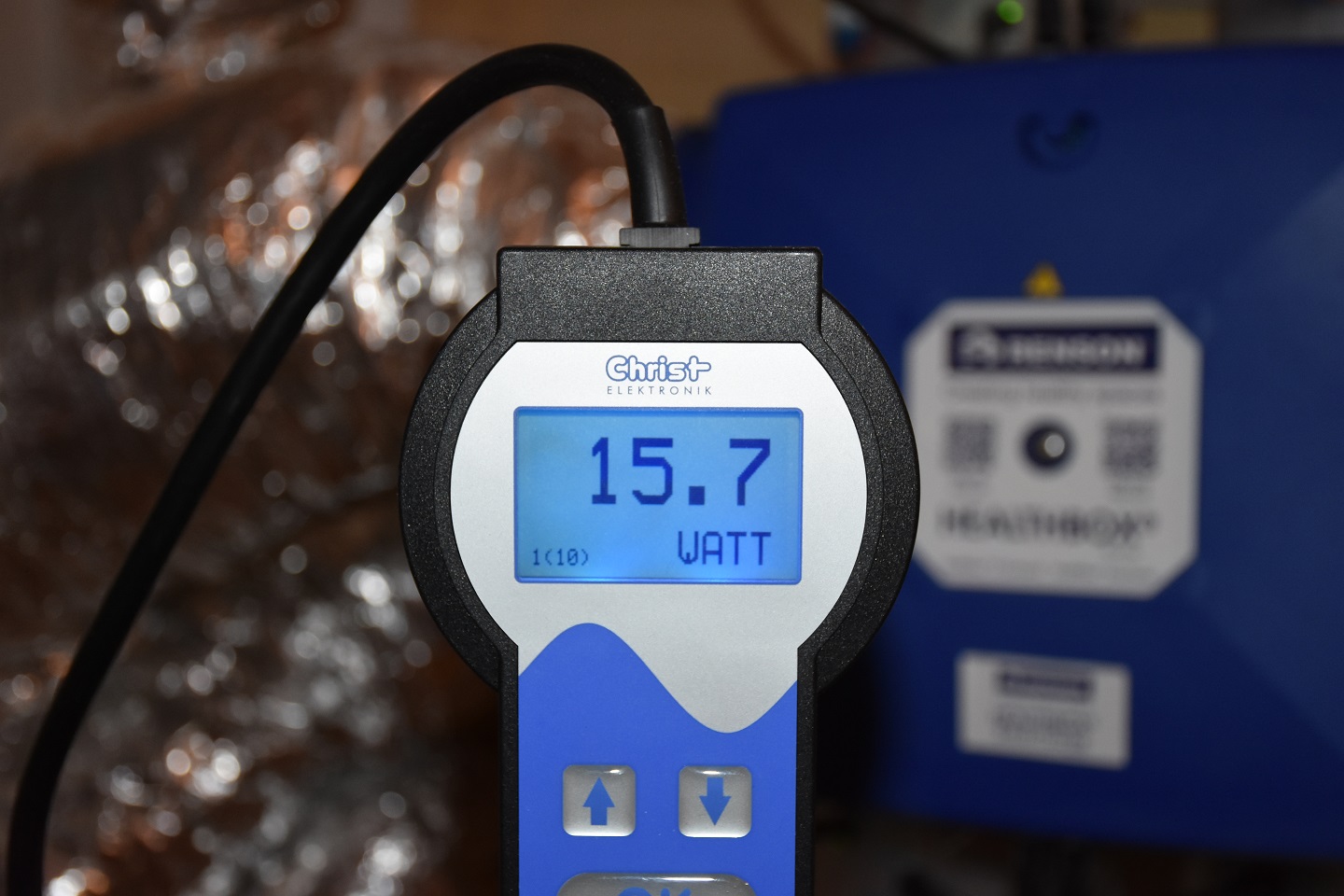
» The measurements are made with calibrated impeller anemometers and power meter
» Can be combined with an airtightness measurement.




